
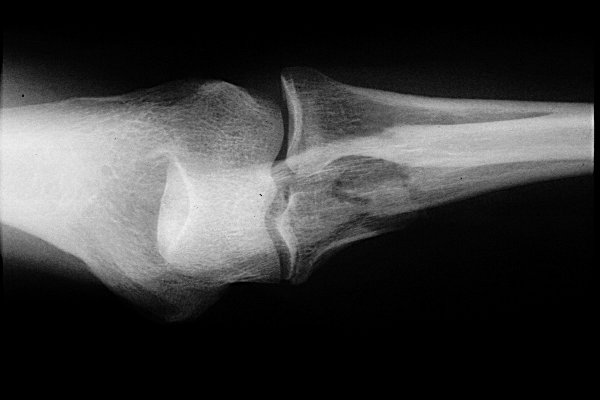
The main cause of Monteggia fracture is trauma. Because at this posture the energy from the radius fracture transmitted towards the radioulnar joint cause the dislocation of the DRUJ. The main etiology of the Monteggia fracture is thought to be a loading may be placed on a forearm during falling onto an outstretched hand (FOOSH) with an extended wrist and hyperpronated forearm. In 1991, Jupiter JB and colleagues from Boston expanded the Bado’s type II description of posterior Monteggia fracture-dislocation. In 1967, Jose Luis Bado, used the "Monteggia lesion" terminology and classified this injury into the four types. In 1803, Giovanni Battista Monteggia, an Italian surgeon, describe the Monteggia fracture as: a fracture of the proximal third of the ulna with the dislocation of the head of radius. Because of children's great capacity to mend their bones, these fractures often have an excellent prognosis. Often, since these fractures are so stable, a simple application of force using one's thumbs is all that is needed for reduction. Monteggia fractures are usually the result of direct trauma to the bone, and are only "partial" fractures, in which the bone does not completely break through. Monteggia fractures is still difficult to diagnose in orthopedic medicine. Forearm fractures lead to significant short-term and long-term disabilities, importantly if they treated incorrectlyor even with some delays. The forearm is an important structure in the human body necessary for the daily living activities. The Monteggia fracture usually are seen in young children commonly younger than 10 years old.
23.3 Life style modifications Ī Monteggia fracture, as an incomplete fracture of long bones, defined as a partial thickness fracture which just the cortex and periosteum are interrupted only on one side of the affected bone.20.7.4.3 metaphyseal unstable extra- or metaphyseal minimal articular involvement.20.7.4 Combination of the above-mentioned techniques.20.7.1 Open reduction internal fixation (ORIF).It is important to use opioids only as directed by doctor. 20.4 Be aware that although opioids help relieve pain after surgery or an injury, they are a narcotic and can be addictive.20.2.1 Complications of open reduction and internal fixation with plates and screws.20.2 Open reduction and internal fixation with plates and screws.20.1.1 Complications of External Fixation.20.1 External Fixation With or Without Percutaneous Pin Fixation.19.2 Complications of Non-surgical therapy.10 Natural History, Complications and Prognosis.5 Differentiating greenstick fracture from other Diseases.Prior to surgery the patient should be informed regarding the possible risk of residual functional limitations and the potential need for further revision surgeries. Negative prognostic factors such as prolonged immobilization, associated coronoid and radial head fractures must be minimized and treated appropriately. The type of fracture and associated injuries such as coronoid fracture and radial head fracture appear to influence the outcome in most cases. Critical analysis with respect to the high rate of complications and unsatisfactory functional outcomes is required. Monteggia fractures are challenging to treat. Open relocation of the radial head and soft tissue procedures are redundant. Rigid anatomic fixation of ulnar fracture is paramount. However, the Monteggia fracture is often still associated with various complications, poor functional outcomes and a relatively high rate of revision surgeries.
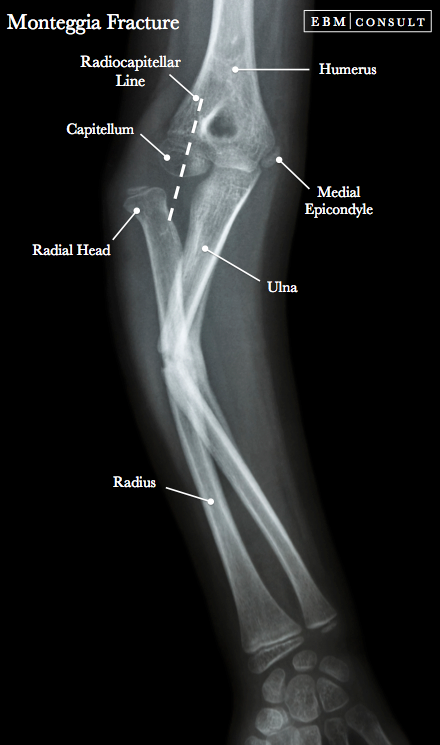
Over the past fifty years, treatment outcomes of traumatic injuries in the upper limb have improved with the advent of better implants.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
